What is WLAN with example
WLAN definition WLAN stands for wireless local area network. It is a wireless connection that connects two or more devices in LAN. WLAN uses access points and routers to make a connection between devices. Wi-Fi is an example of WLAN where devices are connected wirelessly within a limited range. WLAN is made within home, office building, computer laboratory, school building or any college campus. For using Wi-Fi, users [...]
WLAN definition
WLAN stands for wireless local area network. It is a wireless connection that connects two or more devices in LAN. WLAN uses access points and routers to make a connection between devices. Wi-Fi is an example of WLAN where devices are connected wirelessly within a limited range. WLAN is made within home, office building, computer laboratory, school building or any college campus. For using Wi-Fi, users need to enter a password for making a connection to the internet. Wi-Fi connection is made either by using mobile hotspots or by using a wireless modem or wireless router.

Also, check what is the access point and Difference between access point and router.
WLAN vs LAN
Some of the differences between LAN (Local area network) and WLAN (Wireless local area network) are below:-
- LAN involve wired and wireless connection while WLAN is an only wireless connection.
- LAN is secured but WLAN is not secured.
- Mobile connectivity is limited in LAN. In the case of WLAN mobile connectivity is good.
- LAN is less expensive while WLAN is expensive.
- LAN is secured from hackers while WLAN can be attacked by hackers and information can be stolen.
- In LAN the connection is interrupted by using low-quality wires. In WLAN connection is affected by bad weather or signal problems. For solving weak signals we have to use repeaters that enhance the signals.
- LAN is now less known than WLAN because for connecting wireless devices WLAN plays an important role. There are many variants of WLAN devices that make a connection to smartphones, tablets, laptops and workstation.
- In LAN we need Ethernet cables while in case of WLAN Ethernet cables are not required and devices can connect wirelessly.
- LAN depends upon connecting wires to switches and routers while WLAN doesn’t need wires to connect to switches and routers.
- Example of LAN includes connecting workstations in a room or office building. Example of WLAN is connecting nodes (smartphones, tablets, mobile devices, laptops, and computers).
- LAN is faster than WLAN
- If you want to stay in one place then LAN is a good option but if you want to move around different places then WLAN is perfect.
Also check: Advantages and disadvantages of wireless LAN
WLAN vs Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi stands for wireless fidelity and it follows IEEE 802.11 standard. WLAN and Wi-Fi look the same in the sense that both are used for making a wireless connection. Wi-Fi is a type of WLAN. There is other wireless connection also that follows IEEE 802.11 standards. Wi-Fi is an excellent example of WLAN. Devices which use Wi-Fi are considered as WLAN devices. Wi-Fi follows some standards defined in IEEE 802.11 but there are other rules also that is followed by other devices. Wi-Fi is usually considered as IEEE 802.11 standard following technology.
Types of WLAN
Two main types of WLAN are explained below:-
Infrastructure based wireless network:
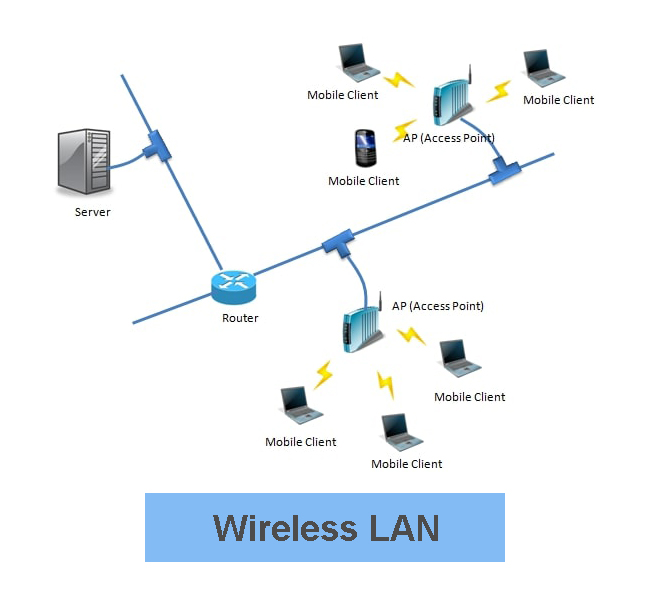
In this type of wireless network, access points (APS) are used to make a connection between devices. An access point connects to router, hub or switch via Ethernet cable and access point uses Wi-Fi signals to share a connection to wireless devices.
Wireless access points make a connection to the terminals (smartphones, tablets, laptops, workstation etc.). In such networks, APS (Access points) works like base station (BS) in cellular systems. The major disadvantage of this network is that it is not portable.

As shown in the picture above, access points are connected to the network switch by wires. And the wireless connection is made between access points and clients (laptop, smartphones, tablets, or workstation)
Adhoc wireless network:
In this type of network, no access points are used and also no wired connection is used. Also, no fixed network parts are used. The example of this type of connection is Wi-Fi hotspot. In the Adhoc network, one device acts as a master and other devices behave as slaves or clients. If you have a device like a smartphone connected via Wi-Fi then you can access the internet within some range. If you move beyond range then the Wi-Fi connection will be disconnected. For example, if you use Wi-Fi in your home and move away from your home then at some distance your Wi-Fi connectivity is lost.

As shown in the picture above, one laptop acts as the source or master to share Wi-Fi and other nodes act as clients or slaves. Wi-Fi connection is shared from source to destination. There are no access points, switch, hub, or routers involved in making the wireless connection. Devices can share a Wi-Fi connection among them. One device acts as a source and other devices act as destination clients.
Example of WLAN
Some examples of WLAN are:-
- Connecting devices through Wi-Fi in home, office, campus, laboratory, school, and college
- Sharing Wi-Fi hotspots from smartphones to other devices like laptops, workstations, etc.
Share this article
Written by : Junaid Rehman
I am a blogger and freelance web developer by profession. I love to blog and learn new things about programming and IT World.
Follow us
A quick overview of the topics covered in this article.




